Minggu, 17 Mei 2009
THE SPUN PRESTRESSED CONCRETE PRODUCT
THE SPUN PRESTRESSED CONCRETE DESIGN AND MATERIALS
The piles are designed as member subjected to axial and flexure. Both axial load and flexure should be considered together because this component is used as part of the foundation, and they support the gravity load as well as the lateral loads which cause bending and shear action on it (earthquake). The codes used as the standard design are JIS A 5335, ACI 543, and Indonesian Concrete Codes (PBI).
Currently concrete design strength range from 50 to 65 MPa. In many cases; however, spun cylinders are made to take advantage of the increased compressive strength due to spinning. The reinforcing steel cage is composed of main and secondary steel. High strength, wire prestressing strand or prestressing wire oriented in the longitudinal direction comprise the main steel reinforcement. Closely spaced spiral steel wire wrapped around the strands provides the necessary secondary reinforcement. The spiral reinforcement, which is normally 5-mm diameter, with yield strength up to 400 MPa, is needed to resist temperature stresses, transfer forces at end parts, and contribute to the torsion and shear strength of the member.
THE SPUN PRESTRESSED CONCRETE DELIVERY
Segmental construction is also used and preferred where it is difficult to transport the full length member or when the poles are to be erected in the congested areas. The poles and piles are made of shorter segments and then assembled at the site using one of several splicing methods..
THE SPUN PRESTRESSED CONCRETE POLE AND PILE
PRECAST CONCRETE WALL PANELS MATERIAL
Architectural precast panels are often made of two types of concrete because of the cost of decorative aggregates and white cement. A backup, or structural, concrete is used for most of the panel thickness, and the concrete for the exposed face of the panel thickness, and the concrete for the exposed face of the panel is selected for its architectural appearance.
PRECAST CONCRETE WALL PANELS FABRICATION AND DELIVERY
- Finish, size and shape of the precast units.
- Method of consolidation.
- Maximum size of coarse aggregate.
- Required comprehensive strength.
- Required surface finish.
- Exposure to severe and the other condition.
Handling and storage procedures should not cause structure damage, detrimental cracking, architectural impairment, or permanent distortion when a panel is being lifted or stripped from the mold, moved to various location for finishing or storage, stored, or loaded or unloaded for delivery and erection. Structural calculation should verify that the panel can be handled in the desired manner, otherwise it should be braced during stripping, handling, transportation and delivery operation.
PRECAST CONCRETE WALL PANELS DESIGN
PRECAST CONCRETE WALL PANELS
PRECAST CONCRETE PRODUCTS
Advanced technology, including robotics and the use of computer aided manufacture, will lead to more efficient erection procedures. The potential for significant reductions in building cost is apparent. The high technology or low labor content aspect make it suitable for any conditions and technological strengths, without necessarily losing the flexibility of construction form that has resulted from mass produced "system building" developed in countries that are technological less advanced.
The advantages of using precast concrete products as building components:
Quality control:
High precision machinery and mould impose a schedule and a discipline. Higher tolerances, more accurate measurements, with less maintenance (because of high performance concrete), and material waste and greater consistency of finishing and results.
Production Control:
Programmed production, time delivery, and/or erection lessen the need for large stock inventoried left in the factory or on the site. Construction is faster on the site where a more efficient order of building components sequences can be maintained.
Inventory Control:
The thight inventory controls possible in a factory setting, over small-piece building material and components virtually eliminates the high rates of theft and vandalism on the site.
Labor Control:
More extensive use of unskilled labor is possible in the factory because of improved supervision (one foreman can adequately supervise more men) and because of the quality control inherent in the machinery or in the factory.
Climate Control:
Factory conditions release certain areas from the "building session" limitation imposed by their climate conditions. A permanent labor force that can be employed when days lost bad weather are minimized also reduces cost of training and initiation to jobs.
Problem Control:
the detailed appraisal of constructional problems before work begins results in fewer delays in construction after commencement on the site.
PRECAST CONCRETE FOR LOW COST HOUSING PROJECT
MARINE STRUCTURES
The use of precast/prestressed concrete for the marine structures provided for the following benefits: (1) giving an aesthetically pleasing structure, (2) low in maintenance for highly functional structure, (3) limited environmental impact, (4) durability in an aggressive marine environment, (4) a fast track construction schedule, (5) a cost effective in an integrated structural system.
FRAME AND SHEAR WALL BUILDING
CONCRETE CORRUGATED SHEET PILE (CCSP)
Prestressed Concrete Corrugated Sheet Piles (CCSP) can be used for port structures, river rieetment, sewerage, earth retaining walls and many other uses and were developed as a substitute for steel sheet piles. Because of there corrugated cross section, CCSP have better capabilities and are cheaper than conventional steel sheet piles. In particular, corrugated sheet piles perform at their best when being driven in; they can be placed with greater accuracy. Many users are already using CCSP and their excellent performance has been highly appreciated. These piles will satisfy for all structural demands.
Materials.
Currently, the specified concrete strength used is 60 Mpa. Prestressing steel used for pretensioned member is either 15.2 or 12.7 mm diameter low relaxation strand with ultimate strength of 1900 MPa. Because the high performance concrete is protected against penetration of oxygen and chloride, durability against corrosion is very high under soil and water condition. High quality of vinyl chloride material is used for expansion joints and water stops, and this can protect spilling sand, leakage of dirty water and grass growing.
Design.
The CCSP is designed based on JIS A 5354-1993
BRIDGE GIRDER

Nearly 50 years have elapsed since precast, prestressed concrete was the first introduced in the construction industry. During this period, precast, prestressed members have been utilized mainly in bridge system. The high quality of precast, prestressed concrete makes it the material choice for short to medium span bridges. Of the system described here, only post tensioned I girders are used with structural "half-slab system" to produce a composite deck system.
PRODUCTION
Bridge girders can be produced segmentally or unsegmentally. The segmental precast girder, or shortened as segmental bridge girder, is a development of the precast system by exploitation of the prestressed implementation system in the manner of the post tensioning. The main purpose of this segmental system is to facilitate the transportation of the members from the plant/ production location to the jobsite. The segmental part length is limited to the maximum of 6 m and the maximum weight of 8 tons so that it can be handled and transported by using light trucks to reach the remote location.
MATERIALS
Selection of the concrete strength and type of prestressing steel is influenced by the type of girder and construction procedure adopted. A concrete compressive strength of 50 MPa is used for the girders since a high degree of quality control is maintained at the precasting plant. Precast concrete slab and diaprragm have a concrete strength in the 30 MPa. Prestressing steel used here is 12.7-mm diameter low relaxation strand with an ultimate strength of 1900 MPa.
DESIGN CONCEPT
Flexural design of prestressed concrete girders is primarily based on the working stress method with the flexural strength checked, similar to the approach taken by American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO) Specification. Design for shear and diagonal tension involves both working stress and strength design calculation. The formulas are somewhat similar to those used in the United States. If the section requires shear reinforcement, it may provide in the form of mild steel reinforcement. Some codes are adopted as the basic design, such as: SKBI-1.3.28.87, Indonesian BMS 1992, Indonesian Concrete Code, ACI 343-77, AASHTO, CP 110-1972.
ADVANTAGES OF CONCRETE CORRUGATED SHEET PILE (CCSP)

High Strength and high quality.
CCSP are manufactured using the highest production techniques in plants where quality control is strictly enforced.
High performance and economics.
High strength material is used. At the same time, the use of corrugated cross section makes them mechanically efficient while reducing weight. This allows PC Corrugated Sheet Piles to be produced very economically.
CCSP have no front or back making handling easier.
Since a PC Corrugated Sheet Pile has no front or back, they can be used in various applications. No special instructions are needed for carrying, temporarily placing or lifting. This makes handling easy and reduces placement errors.
Large CCSP can be manufactured.
Large or long CCSP can be manufactured from prestressed concrete (PC) without problems.
Completely free from rust and corrosion; make them useable even in marine structures.
Since the piles are prestressed, there is no cracking. Also, they can be used for ocean structures in accordance with Standard Concrete Specification requirement, especially sever corrosive environment.
Can be made watertight.
Using newly developed highly elastic vinyl chloride sealing materials, sheet piles can be sealed to prevent sand being sucked out, discoloration from water leaks and growth of weeds joints.
Excellent workability.
Sheet piles can withstand a high tensile force, allowing them to be pulled out after driving; and are suited to mechanical construction work involving many kinds of machines, even vibro hammer, because they are made of prestressed concrete.
High driving accuracy.
Because of corrugated cross section of the sheet piles, resisting planes are large in the lateral direction and the normal direction so that there is less tilting or overturning.
Small displacement (deflection) at the head of sheet piles.
Even in case of self-standing sheet pile retaining walls, the displacement at the head portions is smaller than for other types, because the moment of inertia is large since the cross section is a wave form. This makes higher retaining walls possible.
Kamis, 07 Mei 2009
BEAMBOY BEAM ANALYSIS TOOL
BeamBoy is freeware and is available for download on this page and many others.
E-mail me if you encounter any problems.
RichGetze@yahoo.com
BeamBoy features:
- English or Metric units
- Linear distributed loads
- Selection of beam cross-section from standard sizes
- Assisted calculation of moment of inertia
Version 2.2 features:
- Improved control over printing of reports
- User customization through Preferences file
- Capability to draw graphic output in outline only, rather than color-filled figures
- Fixes of bugs present in version 2.1


Download BeamBoy from this page (1.9 MB)
Or try mirror download at BuildersMatrix.com
CALSD UI

The CALSD program has been developed a decade ago at the University of California, San Diego to support teaching and learning of structural engineering concepts and techniques. This user interface was created as part of a university cooperation project in 1996. For further information please address to the Division of Structural Engineering at the University of California, San Diego.
Calsd.zip - Exectuable Version 3.10 and C++/Fotran source code.FEMAX

Femax is a set of software components for structural analysis using the Finite Element Method (FEM). They can be used with the Component Object Model (COM) and Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) in Microsoft Excel.
Femax.zip - Prototype for Microsoft Windows.BEAMAX
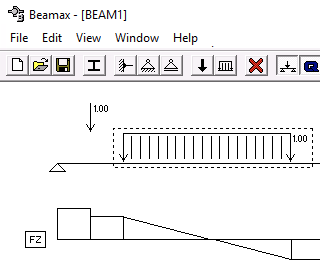
Beamax is an application for visually creating, editing and analysing continuous beams. Fixed, hinged and roller supports and point and distributed loads are supported. Shear force, bending moment and displacement curve is displayed graphically.
Beamax.zip - Executable Version 2.1 for Microsoft Windows.BRIDGE ENGINEERING SOFTWARE - WBFL
| WBFL™ Overview | ||||||||||||||
| The Washington Bridge Foundation Libraries™ (WBFL) provide the foundation upon which WSDOT is building its next generation bridge engineering software tools. The WBFL consists of programmable software components that can be used in spreadsheets and MathCAD documents that you write as well as C++ libraries for those of you write bridge engineering applications. This software has been developed for the Alternate Route Project. The WBFL™ is licensed under the terms and conditions of the Alternate Route Library Open Source License. Under certain circumstances you can develop propriety software that uses WBFL components. Review the license carefully for details. | ||||||||||||||
| Releases | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| Features | ||||||||||||||
The WBFL features the following libraries for use with spreadsheets, MathCAD, and other Automation clients:
The WBFL also contains the following C++ class libraries:
|
Rabu, 06 Mei 2009
BRIDGE ENGINEERING SOFTWARE - BARLIST
| Barlist™ SDK Overview | |||||||||||||||||
| This web site provides documentation for software developers creating Add-in components for Barlist™ Version 4. Barlist™ SDK is licensed with the Alternate Route Open Source License. | |||||||||||||||||
| Releases | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Features | |||||||||||||||||
| Believe it or not, Barlist Version 4 supports add-in components developed by third parties. Why does such a simple little program support such a powerful feature? The need to support add-in components stems from the fact that our users want to generate barlist contract drawings directly from the Barlist program. If we all used the same CAD system, with the same customizations and we promised never to change, generating barlist drawings would be relatively straightforward. In reality we all use different CAD software and those that use the same software have it configured differently. The WSDOT Bridge and Structures Office uses MicroGDS, many of our consultants use MicroStation or AutoCADD. Other CAD systems could conceivably be created at some future time. How can the Barlist program generate barlist contract drawings for a CAD system that doesn’t even exist yet and for an unpredictable set of customizations? The answer is, it can’t. However, through the use of add-in technology, you can develop your own add-in that supports a specific CAD system. Creating barlist contract drawings isn’t the only use of add-in components. The add-in features of the Barlist program are wide open. You can make an add-in do what ever you like. For example, a standard add-in is the BXF File Generator. This add-in creates barlist files in the BXF format found in Version 3 of the Barlist program. Let your imagination guide you. Building Add-ins with Visual Basic Building Add-ins with Visual C++
|
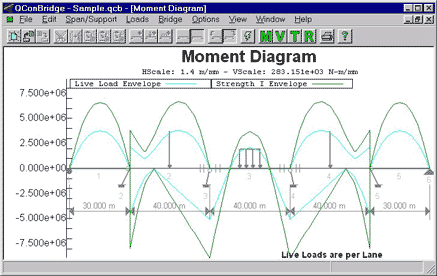
BRIDGE ENGINEERING SOFTWARE - QCONBRIDGE
| QConBridge™ Overview | |||||||||
| QConBridge™ is a live load analysis program for continuous bridge frames. This software has been developed for the Alternate Route Project. QConBridge™ performs live load analysis for the AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specification HL93 live load model. The software accommodates standard and user defined DC and DW dead loads, and performs Strength I, Service I, Service II, Service III, and Fatigue Limit State combinations. QConBridge™ is licensed with the Alternate Route Open Source License. Library Update | |||||||||
| Releases | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Features | |||||||||
|
|
Selasa, 05 Mei 2009
BRIDGE ENGINEERING SOFTWARE - PGSUPER
PGSuper™ is our Precast-Prestressed Girder design and analysis software. This software has been developed for the Alternate Route Project. PGSuper™ can be used to design and check precast-prestressed girder bridges in accordance with the AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specification and/or WSDOT criteria. The flexural design feature computes the number and configuration of prestressing strands and the minimum required concrete release strength. The shear design feature determines the number, size, and spacing of transverse reinforcement for vertical shear, horizontal shear, bursting, and strand confinement. Specification checking evaluates girders for compliance with strength, service, and detailing criteria. Girders are evaluated for stresses and stability during handling and transportation. Temporary prestressing to control camber, improve stability, and reduce concrete release strengths may also be input. The capabilities and constraints of local fabricators have been accounted for in this software product. PGSuper™ has been designed to allow for future expansion and updating as design criteria and user expectations change.
PGSuper™ is licensed with the Alternate Route Open Source License.
Releases
# Preview Version: 2.1.1 Beta 3 May 05, 2009
# Current Version: 2.1.0 February 10, 2009
| PGSuper™ Download Center | |||||||
| Before installing this version please un-install all previous versions of Washington Bridge Foundation Libraries (WBFL), PGSuper, and PGSplice Learn more about PGSuperBridgeSight Software hosts the PGSuper community site PGSuper.com where you can find PGSuper tips, tricks, and on-line training. | |||||||
| |||||||
| | |||||||
Minimum Requirements
| |||||||
| | |||||||
| Required Development Tools If you would like to compile PGSuper from source code, you will need the following commercial development tools.
| |||||||
| | |||||||
| Additional Libraries The following libraries, ActiveX controls, etc, are used by the PGSuper program.
|
BRIDGE ENGINEERING SOFTWARE - PGSPLICE
PGSplice™ is our spliced girder analysis software. This software has been developed for the Alternate Route Project. PGSplice™ can be used to check spliced precast-prestressed girder design alternatives in accordance with the AASHTO LRFD Bridge Design Specification and/or WSDOT criteria. This software is designed to be an companion tool to PGSuper™
PGSplice™ is licensed with the Alternate Route Open Source License.
Releases
# Current Version: 0.7.0 February 10, 2009
| PGSplice™ Download Center | ||||||
| Before installing this version please un-install all previous versions of Washington Bridge Foundation Libraries (WBFL), PGSuper and PGSplice | ||||||
| ||||||
| | ||||||
Minimum Requirements
| ||||||
| | ||||||
| Required Development Tools If you would like to compile PGSplice from source code, you will need the following commercial development tools.
| ||||||
| | ||||||
| Additional Libraries The following libraries, ActiveX controls, etc, are used by the PGSplice program.
|
BRIDGE ENGINEERING SOFTWARE - DFSAP
The computer program DFSAP provides direct assessment of the three-dimensional/rotational spring stiffnesses of an isolated short, intermediate or long pile/shaft or similar stiffness of a pile/shaft group with our without cap. Accordingly, the bridge engineer will be able to assess the various springs of the foundation stiffness matrix with disregard for the complexity of the soil profile, the type and arrangement of piles/shafts, and nonlinear material behavior. Soil liquifaction and the associated induced pore water pressures are considered in the assessed foundation stiffness. Lateral spreading of the soil is an important phenomenon and is also handled by the DFSAP program. The DFSAP program is based on the well established concepts of the Strain Wedge model for laterally loaded piles/shafts and pile groups.
Reference Material
* DFSAP Final Report
* Single Pile Analysis
* Liquefaction
* Cap Shafts
* Axial-Sloping Ground
* Stiffness
WSDOT is not providing support to external users of DFSAP. You may contact the software developers at jpsassoc@aol.com for information regarding support service contracts.
Releases
# Current Version: 1.0 August 09, 2006
| DFSAP™ Download Center | ||||
| | ||||
|
BRIDGE ENGINEERING SOFTWARE - BETOOLBOX
BEToolbox™ is a collection of WSDOT's legacy bridge engineering tools. This software has been developed for the Alternate Route Project.
The goal of the BEToolbox™ is to bring together our legacy applications into an easy to use and convenient tool without having to re-write the programs. We recognize that many of these legacy tools should be completely re-written from the ground up. That will come later.
BEToolkit™ is licensed with the Alternate Route Open Source License.
Releases
# Current Version: 1.6.0 February 10, 2009
Features
When we had these programs running on our VAX system, they were difficult to access and the documentation was difficult to find. It was extremely difficult to share these programs with anyone outside of WSDOT. The programs were also a pain to use because they required you to jump around between the operating system, text editors, and the executable program. Creating input files was always a chore because you had to first find the coding form and them type the data into some cryptic file format.
The BEToolbox™ is a great compromise between the need to re-write the applications and making them more useful and accessible while expending as little effort as possible.
The BEToolbox™ features the following tools:
BOXGIR Section Properties of box girders
COMGIR Computes bending stresses in the top and bottom flanges of a curved composite girder
CURVEL Computes elevations for alignments with horizontal and vertical curves
GIRCOMP Section Properties of Built-up or Rolled Beam composite steel girders
GPILE Computes individual pile loads in a pile group
PSGDES Precast Girder Design and Analysis, Camber and Deflection calculations, and Handling and Hauling Analysis for the AASHTO Standard Specification
TORSION Computes torsional moments of inertia for closed cell box girder bridges and WSDOT standard prestressed girders.
TRSSMEM Computes geometric properties of built-up truss members.
ULT2AX Ultimate Moment Capacity of Reinforced Concrete Sections subject to biaxial bending and axial load
| BEToolbox™ Download Center | ||||||||||
| Before installing this version please un-install all previous versions of Washington Bridge Foundation Libraries (WBFL), PGSuper, PGSplice, Barlist, and BEToolbox. WSDOT has put together a simple batch file to make this easy. Right-click on this link to download the script. Review the script completely before executing as it may not be appropriate for particular circumstance. This script has to be run for every user account that has installed these software programs. | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||
| | ||||||||||
Minimum Requirements
Win 95/98 Users - The BEToolbox™ is developed and testing for the Windows NT operating system. We have made some adjustments to the installer that (hopefully) will enable you to run this software on Win 95/98. Please let us know if you have any difficulties so we can address the problem. | ||||||||||
| | ||||||||||
| Required Development Tools The following commercial development tools where used to build the BEToolbox™ program.
|
BRIDGE ENGINEERING SOFTWARE - BARLIST
Barlist™ - Reinforcing Steel Quantity Estimates. This software has been developed for the Alternate Route Project. Version 4 features an Explorer-style interface for managing reinforcement groups and bar records, an interactive bend guide for selecting bend diagrams, and support for third party add-in components.
Barlist™ is licensed with the Alternate Route Open Source License.
Releases
# Current Version: 4.1 October 01, 2004
| Barlist™ Download Center | ||||||
| Before installing this version please un-install all previous versions of Washington Bridge Foundation Libraries (WBFL), PGSuper, PGSplice, Barlist, and BEToolbox. WSDOT has put together a simple batch file to make this easy. Right-click on this link to download the script. Review the script completely before executing as it may not be appropriate for particular circumstance. This script has to be run for every user account that has installed these software programs. | ||||||
| ||||||
| | ||||||
Minimum Requirements
Win 95/98 Users - Barlist is developed and testing for the Windows NT operating system. We have performed limited testing on the Windows 95 and 98 operating systems. Generally speaking, Barlist will work with Win 95 and 98, however, on rare occasions, Barlist has crashed with certain operating system and browser configurations. If you experience problems with Barlist on Win95/98, please let us know so we can improve our product. | ||||||
| | ||||||
| Required Development Tools The following commercial development tools where used to build the Barlist™ program.
| ||||||
| | ||||||
| Additional Libraries The following libraries, ActiveX controls, etc, are used by the Barlist program.
|
Senin, 04 Mei 2009
BRIDGE ENGINEERING SOFTWARE - RSPBR2
Program RspBr2 is a plane frame structural analysis program to aid bridge engineers in design and checking beam bridges. It is intended to supplement production design programs and be integrated with pre and post processing routines for increased effectiveness and quality control. The flexible text command interface, structure types, loadings, and report combinations should adapt to constantly changing design specifications.
This software was generously contributed to the Alternate Route Project by Phil Rabb, formally of Oregon DOT and David Evans Engineering
Releases
# Current Version: 3.0 April 10, 2006
| RspBr2 Download Center | ||||||
| | ||||||
|
Bridge Engineering Software - RMCalc
RMCalc is a Windows-based software program to compute restraint moments in precast prestressed concrete girder bridges constructed with continuous spans. It uses the same algorithms as BRIDGERM, an older FORTRAN based program written as part of the Transportation Research Board''s NCHRP Report 322.
What are restraint moments?
Precast prestressed concrete girders have a tendency to creep upwards over time due to the prestressing force and other effects. If a girder''s ends are restrained by a pier or diaphragm, forces will build up in the girder due to the creep. Typically, the ultimate restraint moment in a girder is a positive moment. This moment combines with other moments in the girder, creating an increase in the mid-span positive moment and a decrease in the negative moment over the piers. In essence, the continuity of the girder is reduced, and the continuous forces move towards simple-span values.
Why would I want to calculate restraint moments?
Without calculating restraint moments, you don''t know how much of your continuity will be lost during the life of the bridge. Therefore, many designers in the past have designed entirely for simple-span forces, even on bridges that are constructed with continuous spans. By knowing the value of restraint moments in the bridge, a designer can design for continuity, and account for restraint moment effects. Depending on the level of continuity, bridges designed for continuous-span forces can have a more cost-effective design than those designed for simple-span forces
This software was generously contributed to the Alternate Route Project by Mike McDonagh of ABAM Engineering in Federal Way, Washington
Releases
# Current Version: 2.2.2 February 14, 2005
| Software Name: | RMCalc |
| Description: | Calculation of restraint moments in precast prestressed concrete girder bridges constructed with continuous spans. |
| Category: | Concrete Design |
| License Type: | Open Source (Alternate Route Project) |
| Price: | Free on WWW |
| Keywords: | |
| Data Format: | |
| Design Code: | |
| Languages: | English |
| WWW: | http://www.wsdot.wa.gov/eesc/bridge/software/ |
| Publisher: | Washington State Department of Transportation |
| Distributor(s): | Washington State Department of Transportation |
| RMCalc Download Center | ||||||
| | ||||||
|